Track
Track lighting track is commonly available in black or white and typically ships in 2, 4, 6 and 8 foot segments. These segments may be cut in the field if they are too long or joined together with connectors to form longer track runs. Most track today conforms with one of three standards (‘H’, ‘J’ or ‘L’ type). Although the standards are externally similar, each is formed differently inside and will only work with fixtures designed for that specific standard. If you are installing a new system, you should typically use H-type track. If you are adding fixtures to an existing system, it’s important to ensure that you have properly identified your existing track standard before purchasing fixtures or other components. Track is available in single and dual circuit versions. Dual circuit track is slightly more complicated than the more common single circuit version and is not automatically configurable using our wizard. If you have questions about dual circuit track, please call our design assistance line.
Track Connectors
Track runs longer than eight feet will require one or more ‘inline connectors’ between track segments. These will be included automatically when using our ‘build your own track system wizard’, otherwise they should be added manually. Track systems that must turn for any reason should be configured with ‘L’, ‘T’ or even ‘X’ connectors accordingly.
Line voltage Track Heads
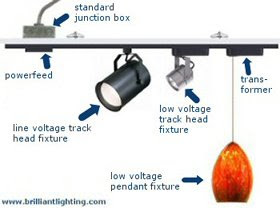
‘Track heads’ are the common spotlight fixtures designed to be attached directly to the track to cast light in any direction. Track heads that use standard, 120 volt bulbs are referred to as ‘line voltage track heads’. Although these fixtures are often quite large, they produce ample light and are very affordable.
Low Voltage Track Heads
Low voltage track heads are rapidly growing in popularity. These heads include an integrated transformer that converts power to a level that allows the use of smaller low-voltage halogen lamps. This results in much smaller fixtures that unobtrusively produce precision accent lighting. Low voltage track heads also consume less power than larger line-voltage styles.
Pendants
Fixtures that hang below the track lighting system on a flexible cable are called pendants. Pendants are used to provide both light and color accents. Although pendants are often installed individually without using a track system (see monopoint lighting) they may also be easily snapped in to a new or existing track system.
Suspension Standoffs
Most track systems are attached directly to the ceiling. In spaces with very high ceilings or exposed ductwork, it may be desirable to suspend the track system below the mounting surface. All track systems may be configured with standoffs of various lengths that will accomplish this quickly and cleanly.
Suspension
Stems Although less common than suspension standoffs, track lighting fixture heights may also be adjusted using suspension stems. Stems and standoffs are different in that standoffs attach between the track and the ceiling to suspend the entire track while stems attach between the track and the fixture to suspend an individual fixture below the track.
Powerfeeds
All track lighting systems must draw power from somewhere. The component that attaches to both the track system and the power outlet or junction box in a room is called the powerfeed. ‘Live end connectors’ are small components that attach to the end of a track run while the more versatile ‘floating canopy connectors’ may be attached anywhere along the track lighting system. Some special installations (often when suspending a track system below an exposed ceiling) will use a ‘BX connector’ that will allow an electrician to power the track system from exposed, shielded conduit wiring (commonly referred to as Romex.)
No comments:
Post a Comment